SMB ERP, a vital tool for small and medium-sized businesses, revolutionizes the way these enterprises operate. From streamlining processes to enhancing efficiency, SMB ERP solutions play a crucial role in driving growth and success. Let's delve deeper into the world of SMB ERP and explore its impact on businesses of all sizes.
What is SMB ERP?
SMB ERP, or Small and Medium-sized Business Enterprise Resource Planning, is a type of software solution designed to streamline and integrate various business processes within small and medium-sized enterprises. It helps in managing key functions such as finance, human resources, inventory, supply chain, and customer relationship management in a centralized system.
Implementing an ERP system in SMBs can bring numerous benefits, such as improved efficiency, increased productivity, better decision-making through accurate data analysis, enhanced collaboration among different departments, and cost savings in the long run.
Key Features and Benefits of SMB ERP
- Centralized Data Management: SMB ERP allows businesses to store all their data in one place, making it easier to access and analyze information across different departments.
- Automation of Processes: The system automates repetitive tasks, reducing manual errors and saving time for employees to focus on more strategic activities.
- Scalability: SMB ERP systems are scalable, allowing businesses to adapt and grow without the need for extensive system changes or replacements.
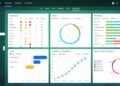
- Improved Reporting and Analytics: With real-time data insights, SMBs can make informed decisions quickly, leading to better business outcomes.
Implementation of SMB ERP

Implementing an ERP system in a Small to Medium-sized Business (SMB) involves a series of steps that are crucial for a successful integration. Despite the benefits that ERP systems can bring to SMBs, there are challenges that may arise during the implementation process.
However, there are also inspiring success stories of SMBs that have effectively implemented ERP solutions to streamline their operations and drive growth.
Steps Involved in Implementing an ERP System in an SMB
- Assessment and Planning: Evaluate current processes, identify business needs, and set clear objectives for the ERP implementation.
- Vendor Selection: Research and choose an ERP vendor that offers solutions tailored to the specific requirements of the SMB.
- Customization and Configuration: Customize the ERP system to align with the SMB's workflows and configure the modules accordingly.
- Data Migration: Transfer data from existing systems to the new ERP platform while ensuring data integrity and accuracy.
- Training and Testing: Train employees on using the ERP system effectively and conduct thorough testing to identify and resolve any issues.
- Go-Live and Support: Launch the ERP system, provide ongoing support, and continuously optimize the system for improved performance.
Challenges Faced by SMBs During ERP Implementation
- Resource Constraints: Limited budget, time, and IT expertise can hinder the smooth implementation of an ERP system in an SMB.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new processes and technologies, leading to resistance and potential disruptions.
- Data Quality and Integration: Ensuring data accuracy and integrating data from various sources can be complex and time-consuming for SMBs.
Successful SMB ERP Implementation Stories
-
Company XYZ, a small manufacturing firm, successfully implemented an ERP system that helped streamline inventory management and production processes, leading to a significant increase in efficiency and cost savings.
-
Retailer ABC integrated an ERP solution that improved customer relationship management and inventory tracking, resulting in a boost in sales and customer satisfaction.
Customization and Integration

Customization and integration play a crucial role in the successful implementation of SMB ERP solutions. Tailoring the system to meet the specific needs of small and medium-sized businesses is essential for maximizing efficiency and productivity.
Importance of Customization in SMB ERP Solutions
- Customization allows SMBs to adapt the ERP system to their unique processes and workflows, ensuring a seamless integration and user experience.
- By customizing the ERP system, SMBs can eliminate unnecessary features and focus on functionalities that are most relevant to their operations, improving overall efficiency.
- Personalized dashboards, reports, and workflows can be created through customization, providing employees with the tools they need to make informed decisions and drive business growth.
Integration with Existing Software and Workflows
- Integrating ERP systems with existing software applications such as accounting software, CRM systems, and inventory management tools is vital for streamlining processes and ensuring data consistency.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) can be used to connect the ERP system with other software solutions, enabling real-time data exchange and automation of tasks.
- SMBs should prioritize compatibility and data synchronization when integrating ERP systems with existing workflows to avoid disruptions and data discrepancies.
Best Practices for Tailoring ERP Systems
- Engage key stakeholders from different departments to gather requirements and insights for customizing the ERP system effectively.
- Focus on training employees on the customized features and functionalities to ensure a smooth transition and maximize user adoption.
- Regularly review and update the customized ERP system to adapt to changing business needs and technological advancements, ensuring long-term success.
Cost Considerations

When it comes to implementing an ERP system in an SMB, cost considerations play a crucial role in the decision-making process. Understanding the various cost factors associated with ERP implementation and comparing the costs of on-premise solutions with cloud-based options can help SMBs make informed choices to manage and optimize their expenses effectively.
Cost Factors in ERP Implementation
- Software Licensing Fees: One of the major upfront costs in implementing an ERP system is the software licensing fees. SMBs need to consider the cost of acquiring the ERP software and any additional modules or features required.
- Implementation Costs: The costs associated with implementing the ERP system, including customization, data migration, training, and support services, should be factored into the overall budget.
- Hardware Infrastructure: For on-premise ERP solutions, SMBs need to invest in the hardware infrastructure to host the system, which can add to the initial and ongoing expenses.
- Maintenance and Support: Ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and support services are essential for the smooth functioning of the ERP system, and SMBs need to budget for these recurring costs.
On-Premise vs. Cloud-Based ERP Solutions
- On-Premise ERP: On-premise solutions require a significant upfront investment in software licenses, hardware, and infrastructure. However, SMBs have more control over customization and data security, but ongoing maintenance and support costs can be higher.
- Cloud-Based ERP: Cloud-based solutions have lower initial costs as they operate on a subscription model. SMBs can benefit from scalability, reduced maintenance requirements, and access to the latest updates without additional expenses. However, customization options may be limited, and long-term costs can add up over time.
Tips for Managing ERP Costs
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly Artikel your business requirements and objectives to avoid unnecessary customization or features that can increase costs.
- Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including upfront costs, ongoing expenses, and potential ROI to make an informed decision.
- Opt for Phased Implementation: Implementing the ERP system in phases can help spread out costs, minimize disruptions, and ensure a smooth transition.
- Regularly Review and Optimize: Continuously monitor and optimize your ERP system to identify cost-saving opportunities, streamline processes, and maximize efficiency.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, SMB ERP stands as a beacon of innovation and efficiency for small and medium-sized businesses. By embracing this transformative technology, companies can navigate the complexities of modern business environments with ease, paving the way for sustainable growth and prosperity.
Q&A
What is SMB ERP?
SMB ERP refers to Enterprise Resource Planning systems designed specifically for small and medium-sized businesses to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and drive growth.
How does SMB ERP differ from ERP solutions for larger enterprises?
SMB ERP solutions are scaled-down versions of traditional ERP systems, tailored to meet the unique needs and budget constraints of small and medium-sized businesses.
What are the key features of SMB ERP?
Key features of SMB ERP include financial management, inventory control, customer relationship management, and reporting tools to enhance decision-making.
How can SMBs integrate ERP systems with existing software?
SMBs can integrate ERP systems with existing software through data migration, API connections, and customization to ensure seamless operations.
What cost considerations are involved in implementing an ERP system for SMBs?
Cost considerations for SMB ERP implementation include software licensing, training, customization, maintenance, and ongoing support.