Exploring the world of process manufacturing ERP, this article delves into the intricacies of implementing, customizing, and managing data within these systems. Dive in to discover how various industries benefit from this technology and the key features that make it a crucial tool for streamlining business processes.
Overview of Process Manufacturing ERP
Process Manufacturing ERP is a specialized type of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software designed to meet the unique needs of process manufacturing industries. Unlike discrete manufacturing, where products are assembled from distinct parts, process manufacturing involves mixing ingredients or raw materials together to create finished goods such as chemicals, food and beverages, pharmaceuticals, and more.
Industries Using Process Manufacturing ERP
- Chemical manufacturing
- Food and beverage production
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Cosmetics production
Benefits of Process Manufacturing ERP
- Improved batch traceability and quality control
- Enhanced inventory management for perishable raw materials
- Optimized production scheduling and planning
- Regulatory compliance and reporting capabilities
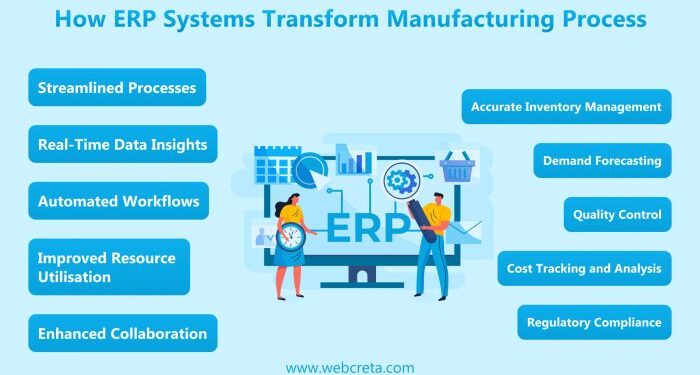
Key Features and Functionalities of Process Manufacturing ERP Software
- Recipe/formula management to ensure accurate ingredient proportions
- Lot tracking and batch genealogy for traceability
- Quality control and compliance monitoring tools
- Inventory management for raw materials, intermediates, and finished goods
- Production planning and scheduling to optimize manufacturing processes
Implementation of Process Manufacturing ERP
Implementing process manufacturing ERP systems involves several key steps that are crucial for a successful integration within an organization. Project managers play a vital role in overseeing the implementation process, ensuring that all aspects are executed effectively and efficiently. However, there are common challenges that may arise during the implementation phase, which need to be addressed proactively.
By following best practices, organizations can ensure a smooth and successful implementation of process manufacturing ERP.
Steps in Implementing Process Manufacturing ERP
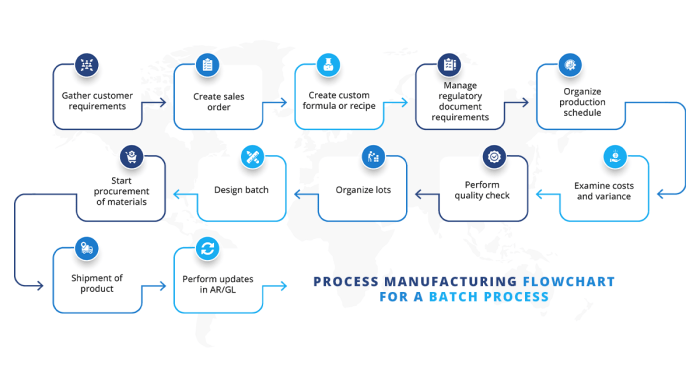
When implementing process manufacturing ERP systems, organizations typically follow a structured approach to ensure a seamless integration. The following are the key steps involved:
- Planning and Preparation
- System Design and Configuration
- Data Migration
- Testing and Training
- Go-Live and Evaluation
Role of Project Managers
Project managers play a critical role in overseeing the implementation of process manufacturing ERP systems. They are responsible for coordinating various activities, managing resources, and ensuring that the project stays on track and within budget. Project managers also act as a liaison between different stakeholders, facilitating communication and resolving any issues that may arise during the implementation process.
Common Challenges in Implementation
During the implementation of process manufacturing ERP systems, organizations may face challenges such as resistance to change, lack of employee training, data integration issues, and scope creep. It is essential to identify these challenges early on and develop strategies to mitigate their impact on the implementation process.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
To ensure a successful implementation of process manufacturing ERP systems, organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Establish clear goals and objectives
- Allocate sufficient resources
- Engage stakeholders throughout the process
- Provide comprehensive training for end-users
- Regularly communicate progress and updates
Customization and Integration
Customization and integration play a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness and efficiency of process manufacturing ERP systems. By tailoring the software to meet specific business needs and seamlessly integrating it with other enterprise systems, companies can optimize their operations and drive growth.
Importance of Customization in Process Manufacturing ERP
Customization in process manufacturing ERP allows companies to adapt the software to their unique processes and requirements. This ensures that the system aligns with the specific workflows and operations of the organization, leading to improved productivity, accuracy, and decision-making capabilities.
- Customized reporting functionalities to generate tailored reports based on specific key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Configurable dashboards to provide real-time insights into production processes and inventory levels.
- Customized workflows to automate and streamline manufacturing processes according to company-specific requirements.
Integration of Process Manufacturing ERP with Other Enterprise Systems
Integration of process manufacturing ERP with other enterprise systems such as CRM, SCM, and financial management software enables seamless data flow and communication across different departments
- Integration with CRM systems to streamline sales and customer management processes.
- Integration with SCM systems to optimize supply chain operations and inventory management.
- Integration with financial management software to ensure accurate financial reporting and cost control.
Impact of Integration on Streamlining Business Processes
The integration of process manufacturing ERP with other enterprise systems leads to increased efficiency, reduced manual data entry, and improved decision-making capabilities. By streamlining business processes and creating a unified data environment, companies can achieve better visibility, control, and agility in their operations.
- Streamlined order-to-cash processes by integrating ERP with CRM for seamless order management and invoicing.
- Improved production planning and inventory management through integration with SCM systems for accurate demand forecasting and supply chain optimization.
- Enhanced financial visibility and control by integrating ERP with financial management software for real-time financial reporting and analysis.
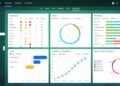
Data Management and Analytics
Data management and analytics play a crucial role in process manufacturing ERP systems. These systems are designed to handle vast amounts of data from various sources and utilize analytics tools to optimize operations and improve efficiency.
Role of Data Management
Data management in process manufacturing ERP involves organizing, storing, and retrieving data efficiently. This includes managing data from production processes, inventory levels, supply chain activities, and customer orders. By ensuring data accuracy and consistency, organizations can make informed decisions based on real-time information.
- Implementing data governance policies to maintain data quality and integrity.
- Integrating data from different departments to provide a comprehensive view of the entire manufacturing process.
- Utilizing data analytics to identify trends, patterns, and opportunities for improvement.
Analytics Tools in Process Manufacturing ERP
Analytics tools are essential for extracting valuable insights from the data generated by process manufacturing ERP systems. These tools help organizations monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and make data-driven decisions to enhance efficiency and productivity.
- Tracking production efficiency and yield rates to optimize manufacturing processes.
- Analyzing inventory levels and demand forecasts to prevent stockouts and overstock situations.
- Monitoring supply chain performance to identify bottlenecks and streamline operations.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are essential metrics that organizations can monitor using process manufacturing ERP analytics to evaluate performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) to measure the efficiency of production equipment.
- Inventory Turnover Ratio to assess how quickly inventory is being sold or used in production.
- On-Time Delivery to track the percentage of customer orders delivered on time.
Final Conclusion
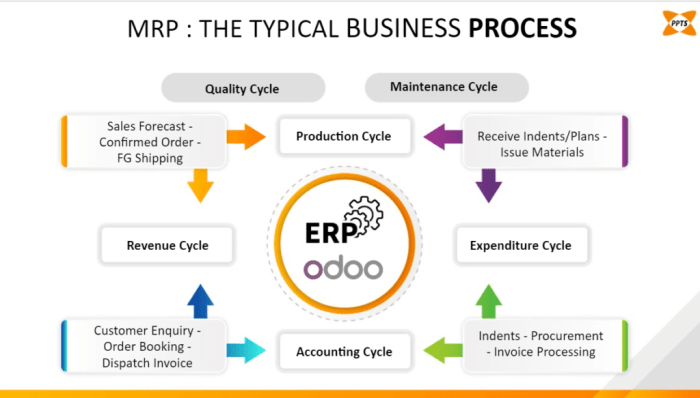
In conclusion, process manufacturing ERP offers a comprehensive solution for industries seeking to enhance efficiency and productivity. By understanding the nuances of implementation, customization, and data management, businesses can leverage this technology to drive growth and success in a competitive market landscape.
FAQ Resource
What industries commonly use process manufacturing ERP?
Food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals are some of the industries that frequently utilize process manufacturing ERP.
What are some common challenges faced during the implementation of process manufacturing ERP?
Integration issues, data migration complexities, and resistance to change are often encountered challenges during the implementation phase.
How can process manufacturing ERP systems be integrated with other enterprise systems?
Process manufacturing ERP systems can be integrated through APIs, middleware, or custom connectors to synchronize data and processes with other enterprise systems.
What role do analytics tools play in optimizing operations within process manufacturing ERP?
Analytics tools help businesses monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to improve operational efficiency and decision-making.